Ever wondered what goes into making sure your medicine stays safe and effective?
Pharmaceutical packaging materials include glass, aluminum, and plastic. Glass is great for chemical resistance, aluminum offers strength and protection from light and moisture, and plastic is versatile and budget-friendly. Each material brings unique benefits that suit various pharmaceutical needs.
Diving into these materials, I remember when I first discovered how crucial packaging is to drug safety. Glass, for instance, isn't just about looking sleek; its chemical resistance makes it perfect for delicate medications. Then there's aluminum, a personal favorite due to its robust nature. It reminds me of how we've helped brands like Matt's by providing leak-proof solutions with our threaded aluminum bottles. And let's not forget plastic—its adaptability and cost-effectiveness make it a staple in the industry. Understanding these materials not only helps in making informed decisions but also ensures that pharmaceuticals reach consumers safely and intact.
Glass is used for its excellent chemical resistance.True
Glass provides a non-reactive surface, ideal for sensitive drugs.
Plastic is the most expensive packaging material.False
Plastic is cost-effective, making it a popular choice for packaging.
Why is Glass Ideal for Pharmaceutical Packaging?
Have you ever stopped to think about why glass is such a go-to for pharmaceutical packaging? Let me take you on a journey to uncover its secrets and why it's a hero in the world of meds.
Glass benefits pharmaceutical packaging by offering excellent chemical stability, impermeability, and transparency. It protects contents from contamination and degradation, ensuring drug safety and efficacy. Its inert nature makes it ideal for sensitive medications.

Chemical Stability and Inertness
Let me tell you about the time I realized just how crucial glass's inert nature is. I was having coffee with a friend who works in pharmaceuticals. She shared a story about a project that involved sensitive medications1. They needed packaging that wouldn't interfere with the drugs' composition, and glass was the only material that fit the bill perfectly. Unlike plastics or aluminum, glass doesn't leach chemicals, keeping medication pure.
| Material | Chemical Stability | Inertness |
|---|---|---|
| Glass | High | Yes |
| Plastic | Low | No |
| Aluminum | Moderate | Partial |
Impermeability and Protection
I remember when I first learned about glass's impermeability. It was during a visit to a pharmaceutical facility. Watching those little vials filled with life-saving medications, I realized how glass acts like a superhero's shield against gases and moisture. It keeps the meds effective by locking out air and moisture that could mess with active ingredients.
Transparency and Visibility
Have you ever peered into a glass bottle to check what's inside? It's like having X-ray vision! In pharmaceuticals, this transparency allows healthcare professionals to inspect medications without opening the package. It's an extra safety net ensuring the quality2 of what patients are about to consume.
Environmental Considerations
Being environmentally conscious is something I hold dear, and glass fits right into that philosophy. It’s 100% recyclable, meaning each bottle could have a second, third, or even hundredth life without losing its quality. This sustainable aspect aligns perfectly with the growing demand for eco-friendly packaging in our industry.
Comparison with Other Materials
While I've seen the durability of aluminum and the flexibility of plastic in action, nothing beats glass when it comes to a mix of stability, transparency, and eco-friendliness. Whether it's preserving product integrity or supporting sustainability, glass stands unmatched.
| Feature | Glass | Aluminum | Plastic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stability | High | Medium | Low |
| Transparency | High | Low | Medium |
| Eco-friendly | Yes | Yes | No |
In summary, choosing glass for pharmaceutical packaging is like picking the best teammate for a mission—someone reliable, protective, and forward-thinking. Understanding these facets helps industry pros make savvy decisions about packaging materials that keep our meds safe and sound.
Glass prevents chemical reactions with medications.True
Glass's inert nature ensures no harmful chemical interactions with drugs.
Plastic is more chemically stable than glass.False
Plastic has low chemical stability compared to glass, which is high.
Why Do We Prefer Aluminum for Certain Medications?
Ever wondered why aluminum is the go-to choice for medication packaging?
Aluminum is favored in medication packaging because it provides an excellent barrier against moisture, light, and contamination while maintaining drug efficacy. Its lightweight and protective nature make it indispensable.

The Protective Nature of Aluminum
You know that feeling when you find the perfect container to keep your leftovers fresh for days? That's how pharmaceutical companies feel about aluminum. Its barrier properties are like a security blanket for medications, shielding them from moisture and light3 that could spoil the active ingredients. It's like having an invisible force field around your medication, keeping it safe and sound.
Versatility and Ease of Use
I remember packing for a long trip and marveling at how I managed to fit everything into my suitcase without it feeling like a ton of bricks. That's the magic of aluminum—it's lightweight yet incredibly strong. Its malleability means it can be shaped into any form needed, making it perfect for various medication types. It's like having a travel-friendly, all-in-one container that meets every need with ease.
Environmental Considerations
If you're like me, always looking for ways to minimize waste, you'll appreciate aluminum's recyclability. It's a material that can be recycled indefinitely without losing quality, making it a hero in our fight against single-use plastics. This aligns perfectly with global sustainability efforts, showing that sometimes, the right choice is also the environmentally friendly one.
Table: Comparison of Material Properties
| Property | Aluminum | Glass | Plastic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barrier Efficacy | High | Moderate | Low |
| Weight | Light | Heavy | Light |
| Recyclability | High | High | Variable |
| Customization | High | Moderate | High |
These properties underscore why pharmaceutical companies increasingly prefer aluminum for medication packaging. Incorporating aluminum not only enhances drug safety but also supports sustainable practices. Its role in vaccine packaging4 is particularly significant, as it ensures product integrity from production to administration.
Aluminum is impermeable to gases.True
Aluminum's impermeability ensures medication stability by blocking gas penetration.
Plastic has better barrier properties than aluminum.False
Aluminum provides superior barrier protection against moisture and light compared to plastic.
What Are the Advantages of Using Plastic in Drug Packaging?
Ever wondered why plastic is often the go-to for drug packaging? It’s not just about keeping costs low or following a trend.
Plastic drug packaging is lightweight, durable, and cost-effective. It offers superior moisture and contamination protection compared to glass or aluminum, enhancing drug safety and shelf life. Its flexibility supports innovative design solutions.
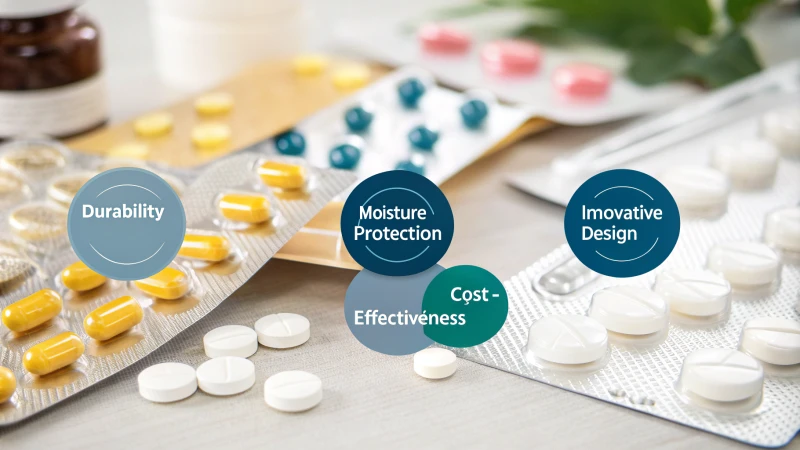
The Cost-Effectiveness of Plastic
When I first started exploring the world of packaging materials, I was amazed at how cost-effective plastic can be. It's like when you're shopping for groceries and find that perfect balance between quality and price. Plastic offers that for manufacturers, making it a budget-friendly choice without sacrificing quality. Compared to glass or aluminum packaging5, it’s usually cheaper to produce, allowing companies to keep costs in check.
| Material | Cost | Durability | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic | Low | High | Moderate |
| Glass | High | Moderate | Low |
| Aluminum | Moderate | High | Low |
Durability and Safety
Remember that time I dropped my phone, and it miraculously survived without a scratch? That’s kind of how I think about plastic in drug packaging. Its durability means that unlike glass, which can shatter into a thousand little pieces, plastic remains intact. This resilience is crucial for protecting drug integrity during transit and storage. Plus, it provides excellent barriers against moisture, which is vital in preserving a drug's potency.
Flexibility in Design
Plastic’s flexibility is like having a wardrobe full of mix-and-match outfits. It allows for all sorts of creative designs, from child-resistant caps to tamper-evident seals. These innovations are essential for maintaining safety standards and enhancing user experience. Plastic’s malleability6 makes it an attractive option for developing packaging solutions that are both practical and visually appealing.
Environmental Considerations
I know plastic often gets a bad rap when it comes to the environment. Trust me, as someone who’s very conscious about sustainability, I get it. But I've seen firsthand how advancements in biodegradable plastics7 and recycling are changing the game. Many pharmaceutical companies are now opting for more eco-friendly plastic options, showing that it's possible to marry sustainability with practicality.
Exploring how pharmaceutical companies8 are adopting these sustainable practices could provide more insights into this evolving landscape.
Comparative Analysis with Glass and Aluminum
In the packaging world, it feels a bit like a friendly rivalry among materials. While glass shines with its chemical resistance and aluminum stands out for its barrier against light and oxygen, plastic’s lightweight nature helps cut down on transportation costs and energy use. This efficiency makes plastic a compelling choice for drug packaging.
For those interested in delving deeper into the material differences, consider exploring how packaging materials9 impact drug shelf life and safety features.
Ultimately, plastic continues to play a significant role in pharmaceutical packaging due to its versatility and advantages, positioning itself as a preferred choice for many in the industry.
Plastic drug packaging is more cost-effective than glass.True
Plastic production costs are lower than glass, reducing overhead.
Plastic offers better chemical resistance than aluminum.False
Glass provides superior chemical resistance compared to plastic.
How Do These Materials Comply with Regulatory Standards?
Ever wondered how everyday materials like glass, aluminum, and plastic navigate the complex world of regulatory standards?
Glass, aluminum, and plastic meet regulatory standards through rigorous testing and certification processes, ensuring adherence to safety, environmental, and quality guidelines. These materials undergo evaluations to comply with both local and international regulations, securing their place in sustainable and safe product packaging.

Glass Compliance with Regulatory Standards
When I think about glass, I remember my grandmother's pantry filled with jam jars—each one spotless and safe enough to be reused year after year. Glass's non-toxic nature10 is a major reason why it's favored across the board. From the FDA's regulations for food contact to the infinite recyclability of glass, it aligns perfectly with stringent environmental directives. The beauty of glass is that it can be recycled endlessly without losing its purity or quality.
Key Benefits:
- Recyclability: Infinite recyclability supports sustainable practices.
- Safety: Naturally non-reactive, maintaining the integrity of contents.
Aluminum's Regulatory Alignment
Ah, aluminum! It always reminds me of those camping trips where carrying light yet sturdy cans made all the difference. Aluminum's approval for direct food contact by the FDA, combined with its lightweight nature that reduces carbon emissions during transportation, makes it a regulatory champion. Its corrosion resistance11 adds another layer of reliability, especially critical when it comes to pharmaceuticals.
Advantages:
- Lightweight: Minimizes transportation emissions.
- Corrosion-resistant: Ensures product integrity.
Plastic and Compliance Challenges
Plastic—now there's a material that sparks a lot of debate. With stringent regulations like those set by the EPA, compliance varies significantly depending on the type of plastic. I remember how bioplastics were once a topic of heated discussion at an industry conference; their potential to reduce reliance on fossil fuels makes them an intriguing option for future compliance strategies.
| Plastic Types & Compliance: | Type | Compliance Focus | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET | Recyclability | Widely recyclable | |
| HDPE | Low environmental impact | Strong and durable | |
| Bioplastic | Sustainability | Reduces fossil fuel reliance |
Understanding these frameworks is crucial for businesses like mine in ensuring that our packaging choices not only meet compliance standards but also support environmental and quality objectives. Diving into material-specific regulations12 can provide deeper insights into creating robust compliance strategies across various applications.
Glass is infinitely recyclable without quality loss.True
Glass retains its purity and quality through endless recycling cycles.
All plastics meet the same regulatory standards.False
Plastic compliance varies by type, with different standards for each.
Conclusion
Pharmaceutical packaging utilizes glass, aluminum, and plastic for safety and efficacy. Each material offers unique benefits: glass for chemical resistance, aluminum for moisture protection, and plastic for cost-effectiveness.
CPI is a professional supplier of aluminum packaging in China over 10 years, if you are looking for an aluminum bottle for medicine, please contat us freely.
-
Discover how glass's inert nature makes it an ideal barrier against chemical reactions in sensitive medications. ↩
-
Learn why glass's transparency adds safety by allowing visual inspection of pharmaceutical products. ↩
-
Discover how aluminum protects medications from moisture and light, maintaining their stability and potency. ↩
-
Explore the critical role of aluminum in maintaining the efficacy and safety of vaccines during storage and distribution. ↩
-
Discover why aluminum is considered a sustainable alternative to plastic, with benefits like recyclability and strength. ↩
-
Learn how plastic's flexibility supports innovative designs such as child-resistant closures and easy-open systems. ↩
-
Explore new developments in biodegradable plastics that address environmental concerns associated with traditional plastics. ↩
-
Understand how leading pharmaceutical companies are integrating sustainability into their operations with innovative packaging solutions. ↩
-
Gain insights into how different packaging materials influence the safety and efficacy of pharmaceuticals. ↩
-
Discover the FDA guidelines that ensure glass used in food packaging is safe and non-toxic. ↩
-
Learn about aluminum's natural corrosion resistance that protects product quality over time. ↩
-
Gain insights into various material-specific regulations crucial for packaging compliance. ↩






